 |
 |
Version: 1.6
Date: 08/23/05
- 1 Introduction
- 2 Installation
- 2.1 Hardware Requirements
- 2.2 Install from ISO
- 2.3 Install to an existing CentOS
3.5 system
- 3 Configuration
- 3.1 Quick start
- 3.1.1 Set an IP address for your
Asterisk@Home box
- 3.1.2 Configure an extension
- 3.1.3
Configure a trunk for outbound and inbound calls
- 3.1.4
Configure Outbound Routing
- 3.1.5 Configuring Incoming Calls
- 3.2 PSTN interface cards
- 3.2.1 FXO Cards
- 3.2.1.1 Digium Wildcard X100P OEM
FXO PCI Card
- 3.2.2 FXS Cards
- 3.2.2.1 Digium TDM400P FXO/FXS Card
- 3.2.3 T1/PRI Cards
- 3.3 VOIP Service Providers
- 3.3.1 Free World Dialup (FWD)
- 3.3.2 VoicePulse
- 3.4 Additional feature not
installed by default
- 3.4.1 FAX to E-mail
- 4 Phones
- 4.1 Soft phones
- 4.1.1 X-Ten
- 4.1.2 sipXphone
- 4.2 Hard phones
- 4.2.1 Cisco 7960/7940
- 4.2.1.1 Setting up a Cisco phone step by step
- 4.2.2 Polycom
- 5 Configuring and using Asterisk@Home features
- 5.1 Conferencing
- 5.1.1 External access to conferences
- 5.2 AMP (Asterisk Management Portal)
- 5.3 DHCP server
- 5.4 Flash Operator Panel
- 5.5 FTP server (vsftpd)
- 5.6 Cisco XML Services
- 5.7 Music On Hold (mpg123)
- 5.8 Fax support (SpanDSP)
- 5.9 xPL
- 5.10 Sugar CRM
- 6 Asterisk@Home add-ons
- 6.1 Click-to-Dial using Microsoft Outlook and AstTapi
- 6.2 H.323 add-on
- 6.3 Webmin - web based Linux management
- 7 Non-standard Hardware
- 7.1 VIA EPIA 800 mhz board (586 board)
- 8 Useful Info for Asterisk@Home
- 8.1 Feature Codes - List
1
Introduction
Asterisk@Home was created to make installing Asterisk easy. Experimenting with
Asterisk should be fun and not take hours or days to set up.
2
Installation
2.1
Hardware Requirements
The faster the system you use to run Asterisk the more simultaneous calls it
will be able to handle a 500MHz PIII with 128 Megs of RAM should easily meet the
needs of the average home use.
2.2
Install from ISO
Download the latest ISO from http://asteriskathome.sourceforge.net and
burn it to a CD
Insert the newly created CD into the CD ROM drive of the system on
which you want to install Asterisk@Home. Reboot the system
and press Enter when prompted.
![[Warning]](./stylesheet-images/warning.png) | Warning |
|
This will erase all data on the hard drive of the PC!!!
|
After Linux has loaded, the CD will eject. Remove the CD from the system and
wait for the system to reboot. Booting the system might take a while, depending
on the speed of your computer. It is necessary for the system to build
from source, so be patient.
Once this process is complete, log in to your new Asterisk@Home system with the
following username and password:
(userUser: root, password: password)
![[Warning]](./stylesheet-images/caution.png) | Caution |
|
Change your root password immediately by typing passwd as
this minimizes the chance of your
Asterisk@Home system being hacked!! |
2.3
Install to an existing CentOS
3.5 system
If you have problems with the ISO you can install onto an existing CentOS server.
Download CentOS
3.5 ISOs from the
CentOS Mirrors
Make a directory to install from, put the install file there, and install.
mkdir /var/aah_load
cp asteriskathome-1.5.tar.gz /var/aah_load
cd /var/aah_load
tar xvfz asteriskathome-1.5.tar.gz
./install.sh
3
Configuration
Once you have installed your
Asterisk@Home system you can start the configuration process. First
register a phone to an extension. Next configure a trunk to
make outbound calls and receive incoming calls.
3.1
Quick start
3.1.1
Set an IP address for your
Asterisk@Home box
To configure Asterisk@Home you will need access to the Web GUI.
If you log into the
console you will get a message which displays the IP address of your Asterisk@Home
system.
If
this field is blank then you have a problem with the network card. Type netconfig
at the command line. This will allow you to set a static IP address for your
Asterisk@Home
box.
After you have configured your network card reboot the system by typeing reboot. Your system will
restart and you should be able to connect to your system from any web browser on
your network.
3.1.2
Configure an extension
Go to a pc on your network with a web browser and connect to your
Asterisk@Home box.
Click on Asterisk Management Portal (user: maint, pass: password) and then setup. Click
Extensions then Add
Extension. Use the default extension 200 and type in a password for registration
like "abc123". then enter the name of the person using this extension.
Go down to the voicemail section and enter a voicemail password. Use
something
you can type on a phone keypad like '1234'. Enter an e-mail address where you
would like your voice messages sent and click add extension. Then click
on the red apply bar at the top of the screen.
Set up a phone for this extension. Get a SIP phone an X-Ten soft phone
is good for testing. See the section on the X-Ten phone. remember to use your
extension and extension password.
Make a call from your phone.
(try *45 this is a local echo test)
3.1.3
Configure a trunk for outbound and inbound calls
Using AMP (user: admin, pass: password) select setup then
trunks. Click on the type of trunk you want to create. See the VOIP
Service Providers section for how to configure a trunk for your provider.
3.1.4
Configure Outbound Routing
Next you need a route to allow calls from your phones to go out on a trunk. If
you have more than one trunk you can set up rules to determine how a trunk is
chosen for each call. Here we will set all calls to go out one trunk.
Using AMP (user: admin, pass: password) select setup then
Outbound Routing. Type in a name for your route. Then enter the
following in the dial
pattern box.
1NXXNXXXXXX
NXXNXXXXXX
NXXXXXX
This will set all calls to use this route.Next go to the Trunk Sequence
section. Drop down the box and select the trunk you configured earlier.
Click add.
That's it. Click Submit Changes and then click on the red apply bar at the top of the screen.
Try dialing a number on your phone like 19197543700 (RedHat customer support)
and you should hear "Welcome to RedHat"
3.1.5
Configuring Incoming Calls
Next you need a route to allow calls from your provider to go someplace.
Using AMP (user: maint, pass: password) select setup then
Incoming Calls. Under the Send Incoming Calls from the PSTN to:
section drop down the
box next to Extension: and select the extension 200 you created
earlier.
Click Submit Changes and then click on the red apply bar at the top of the screen.
Call the phone number from your provider with a cell phone or other non-IP
phone. Your SIP phone at extension 200 should ring.
3.2
PSTN interface cards
There are may type's of PSTN interface cards. These can include a single FXO
card the allow 1 home telephone line to be connected to Asterisk, or a T1 card
that allows a digital trunk to be connected to Asterisk. All of these cards
allow you to make calls directlly on the Public Switch Telephone Network without
have to use a VOIP phone service provider.
PSTN cards and also be used to connect PSTN (Non VOIP) phone to Asterisk.
These can include a single FXS card the allow 1 home telephone to be connected
to asterisk, or a T1 card that allows a Channel bank with 24 phones or a tie
line to a PBX to be connected to Asterisk.
3.2.1
FXO Cards
These cards allow you to connect a POTS (plain Old Telephone System) line to
your Asterisk@Home box.
3.2.1.1
Digium Wildcard X100P OEM
FXO PCI Card
These voice modems are available on e-bay for about $10.00 They are not made by Digium and are of low quality. Having said this they can work very well in many
situations. If your phone line is well balanced there will work well. If itís
not you can get some bad echos. We recommend them only for testing not for a
production system.
To configure these cards for use with Asterisk@Home first use the zaptel card
auto-config utility to set up the zaptel driver.
Type genzaptelconf -s -d from the command line (if the card was in the
system when you installed aah this already done)
Next go into the AMP web interface and create a trunk.
There is already a trunk called ZAP/g0 edit this
Enter the phone number for you pots line in the Caller ID field
Enter 1 for Maximum channels
Set a dial rule if you want for this trunk
Select an outbound dial prefix to select this trunk when dialing
Set the Zap Identifier to 1 (the default is g0)
This trunk is now configuredyou must add a route for incoming calls or
asterisk will not answer this line
click on incoming calls in amp and set up an incoming route.
to make outbound calls you will need an outbound route. set one up in AMP
3.2.2
FXS Cards
These cards allow you to connect an Analog phone to your Asterisk@Home box.
3.2.2.1
Digium TDM400P FXO/FXS Card
This card has 4 module ports that can be loaded with FXS or FXO mudules. You can auto config this card just like the X100P.
Channel 1 is the top RJ-45 on
the back of the
TDM400P card.
To configure these cards for use with Asterisk@Home first use the zaptel card
auto-config utility to set up the zaptel driver.
Type genzaptelconf -s -d from the command line (if the card was in the
system when you installed aah this already done)
Next, using config edit, look in the zapata-auto.conf file you will see a list of all your channels.
Set up the trunks as trunks and the extensions as extensions in AMP.
For example if your zapata-auto.conf file looks like this
; Span 1: WCTDM/0 "Wildcard TDM400P REV E/F Board 1"
signalling=fxo_ks
; Note: this is an extension. Create a ZAP extension in AMP for Channel 1
channel => 1
signalling=fxs_ks
; Note: this is a trunk. Create a ZAP trunk in AMP for Channel 2
context=from-pstn
channel => 2
then add a zap extension for channel 1 and a zap trunk for channel 2
you may have to reboot your system to get everything going.
you must add a route for incoming calls or asterisk will not answer your
trunk
click on incoming calls in amp and set up an incoming route.
to make outbound calls you will need an outbound route. Set one up in AMP.
3.2.3
T1/PRI Cards
Setup for
Digium T100P and a PRI
login to the CLI as root
[root@asterisk1 /]# cd /etc
[root@asterisk1 etc]# nano -w zaptel.conf
Add these lines to /etc/zaptel.conf
span=1,1,0,esf,b8zs
bchan=1-23 # set this to 1-15,17-31 for E1
dchan=24 # set this to 16 for E1
Add # to front of fxsks=1 so it looks like this:
span=1,1,0,esf,b8zs
bchan=1-23 # set this to 1-15,17-31 for E1
dchan=24 # set this to 16 for E1
#fxsks=1
loadzone = us
defaultzone=us
Control-X then Y to save zaptel.conf
Log into Asterisk@home using a browser http://-asterisk-ip-adress/admin
Then click on Maintenance
Then click on Config Edit
Then click on zapata.conf
Comment out with ; to signalling=fxs_ks:
;signalling=fxs_ks
Then copy just below it:
signalling=pri_cpe ; pri_cpe = PRI slave ; pri_net = PRI master
switchtype=national
Then add this callerid=asreceived under ;usedistinctiveringdetection=yes
Change echocancelwhenbridged=yes
Change echotraining=400 ; Asterisk trains to the beginning of the call,
number is in milliseconds
at the end of the file copy and past:
channel => 1-23 ; Set this to 1-15,17-31 for E1
Click Update and Click Re-Read Config
Go back to SSH root
[root@asterisk1 etc]# modprobe wct1xxp
[root@asterisk1 etc]# ztcfg -vv
Do a shutdown and restart the system
[root@asterisk1 etc]# shutdown -r now
You just need to login via web and make your setup.
3.3
VOIP Service Providers
There are many service providers. Some provide
proxy server that make it possible
to connect to other members of that provider. Other providers offer both
incoming
and outgoing PSTN to VOIP termination. Here are a few common providers and how to
make the work with Asterisk@Home.
Most providers will give you phone number and a password for that provider some
will also give you a user name. If you get a real PSTN number from the provider
it will be a normal 10 digit number (US providers). some providers give out shorter
number that can only be used by other members of that provider.
3.3.1
Free World Dialup (FWD)
Contact: http://connect.voicepulse.com/
Service: proxy to other FWD users, Gateway to other providers
Protocol: SIP or IAX
Cost: free
You should have a phone number (123456) and a password (wibble). You also need to
have your FWD account setup for IAX. This is achieved by visiting
http://www.freeworlddialup.com,
logging in and turning on IAX. It does take a little bit of time to be set up (10
mins or so), so do that first. Once you've turned it on and clicked 'Submit' enough
times (I noticed I had to click Submit two or three times before it came up with
'Changes Successful', that may have just been a temporary glitch) you're ready to
proceed below.
Once again, you need to be in AMP, the Asterisk Management Portal. Click on Setup
up the top, but this time click on Trunks on the left. Click on Add IAX2
Trunk
Dial Prefix is, usually, 393 ó That's 'FWD' on your phones pad.
Leave Default Trunk switched off
Outbound Caller ID should (but doesn't have to be) set to your FWD Number.
This is what is displayed when you call someone else through FWD. They'd normally
just see your Extension (200).
Outgoing SettingsTrunk Name: fwd (This is just a descriptive
name, and is what appears on the left of the screen)
PEER Details: (Change '123456' and 'wibble' to be your FWD Number and
Password)
host=iax2.fwdnet.net
type=peer
username=123456
secret=wibble
Incoming Settings
USER Context: iaxfwd (Pay attention here. Don't change it. or it won't
work)
USER Details (Nothing needs to be changed here, this can be pasted
straight in)
allow=ulaw
auth=rsa
context=from-pstn
disallow=all
inkeys=freeworlddialup
type=user
Register String: should be set to yournumber:yourpassword@iax2.fwdnet.net,
using our examples above, it would be 123456:wibble@iax2.fwdnet.net
Thats it. Click on Submit Changes, and then on the big red 'You have made
changes' bar and you're done.
Assuming you've got your username and password correct, you should now be able to
dial '393612', Which will read out the time to you. IF you're feeling exceptionally
brave, call '393613', which is a useful little echo tester - it'll just bounce back
to you everything you say to it. Ycan then try '393514' which is FWD's 'Coffee Lounge'
- I've never actually sucessfully had a conversation with anyone there, however,
or '39355555', which calls a random volunteer, so you can actually speak to a live
person!3.3.2
VoicePulse
Contact: http://connect.voicepulse.com/
Service: PSTN termination
Protocol: IAX
Cost: pay
Once again, you need to be in AMP, the Asterisk Management Portal. Click on Setup
up the top, but this time click on Trunks on the left. Click on Add IAX2
Trunk
Dial Prefix 9 if your not alredy
Leave Default Trunk switched off (or make this the default if you want all
your calls to use it)
Outbound Caller ID should (but doesn't have to be) set to your VoicePulse
Number.
Outgoing SettingsTrunk Name:
voicepulse-out-01
(This is just a descriptive name)
PEER Details: (Change <your username> and <your password> to be your
VoicePulse Number and Password)
host=gwiaxt01.voicepulse.com
secret=<your password>
type=peer
username=<your username>
Incoming Settings
USER Context: voicepulse-in-01 (Pay attention here. Don't change it.
or it won't work)
USER Details (Nothing needs to be changed here, this can be pasted
straight in)
auth=rsa
context=from-pstn
inkeys=voicepulse01
type=user
Register String: should be set to <your username>:<your password>@gwiax-in-01.voicepulse.com
example (bob:abc123 @gwiax-in-01.voicepulse.com)
Thats it. Click on Submit Changes, and then on the big red 'You have made
changes' bar and you're done.
For a test make a call (try 1-800-555-1212)
3.4
Additional feature not
installed by default
Some of the features of Asterisk@Home are not installed by default. Here are
the steps to install them.
3.4.1
FAX to E-mail
Type install-pdf from the Linux command line. This will install support for
encoding incoming faxes as PDFs and e-mailing them.
4
Phones
VOIP phones vary widely in price, features, and sound quality. Phones support
either SIP or IAX protocol. For simple testing a free soft phone like X-ten is good.
For day to day use a good hard phone is the best. Grandstream makes a cheap easy
to configure phone with good quality and feature. Polycom and Cisco make the best
phones with the highest sound quality and feature. If you have and existing analog
phone like a cordless that you want to use and ATA will convert an analog phone
to SIP.
4.1
Soft phones
Soft Phones run on a host computer and use the computer speaker and mic or a
headset for voice. Soft phones are available for most operating system.
4.1.1
X-Ten
One of the easiest to setup is X-Lite. X-Lite is available for free from
http://www.xten.com.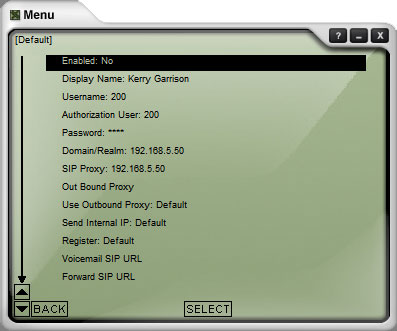
If X-Lite cannot connect, the setup screen should open, if not, click on the
"drop down" icon just to the left of the green Off-Hook icon.
Under System Settings, select the SIP Proxy settings, then
double-click on the first entry. You will see the SIP Proxy settings as shown
here. The settings I changed are as follows:
Username: 200 (my extension)
Authentication User: 200 (my extension again)
Password: 1111 (my extension password)
DomainRelm: 192.168.5.50 (PBX IP address)
SIP Proxy: 192.168.5.50 (PBX IP address)
The sipXphone project,
formerly known as Pingtel's instant xpressa
soft phone, is a fully functional SIP soft phone that runs on Microsoft Windows
and Linux. The Pingtel's xpressa phone (no longer a Pingtel product) is based on
this same source base. Windows Download from
http://www.sipfoundry.org/pub/sipXphone/win32/
4.2
Hard phones
4.2.1
Cisco 7960/7940
The Cisco SIP IP Phone software allows businesses and service
providers to use the Cisco 7940 and 7960 IP Phone platforms in any standard SIP
network. The SIP software provides for both on-board traditional desktop services
such as Caller-ID, Call Hold, Call Transfer, 3-Way Calling, and Call Waiting as
well as an XML interface to allow for enhanced web based services. The XML interface
allows the phone to transcend the traditional phone paradigm and become a true Internet
appliance. By supporting web browsing type functionality as well as allowing for
application developers to directly control the user interaction on the phone and
integrate tightly with the Cisco SIP phone, the Cisco SIP phone is a key enabler
of enhanced and rapid application deployment in any SIP customer's network.
Type setup-cisco from the command line to set up
a basic SIPDefault.cnf in the /tftpboot directory.
Copy your Cisco 7.4 SIP firmware into the /tftpboot
directory using WinSCP.
using the Cisco config tool in the maint menu to set up
your phone.
4.2.1.1
Setting up a Cisco phone step by step
Connecting a Cisco 7960/7940 to your Asterisk@Home. The easiest way to use these phones with
Asterisk@Home is with the SIP firmware.
Power on your phone and connect it to your network. You will need to change the IP address of your phone to a free one on your network or enable DHCP is you have a DHCP server.
Unlock your phone by pressing **# (for old firmware) or selecting
unlock config from the config menu and type in the password
(default is 'cisco')
Change the IP address or enable DHCP. Enter the IP address of your Asterisk@Home box in the TFTP server field. If DHCP is enabled you will have to select alternate TFTP server = yes so you can edit the TFTP field.
Get the latest firmware for the Cisco phone (7.4) and copy the files firmware files to your Asterisk@Home box. Put them in the
/tftpboot directory.
Create a Default.cnf file by using the setup-cisco command and change the file permissions on the firmware files that you uploaded in the last step. Type the following.
setup-cisco
chmod 777 /tftpboot/*
Add a Cisco config file for your phone. Use the wed GUI and click maintenance -> Cisco Config -> Create
a new phone configuration file.
Type in the mac address of your phone. Itís located on the bottom of your phone. (starts with 00) Enter a name for your phone in the Phone Label box. Enter
200 in the Line Name and the Display Name fields for Line 1. Click
add.
Click on Edit phone configuration files and click edit next to your phone. Go to
Line 1 and type 200 in the Auth Name box. Then enter a password like abc123 in the
password box. Click change.
Create extension 200. setup -> extensions use abc123 for the extension password.
Reboot your phone by disconnecting the power or pressing *-6-settings.
Your phone should upload the new firmware and extension. Make a test call like *65.
Trouble shooting: The Cisco phone can be difficult to upgrade. If your phone does not seem to upload the firmware try this. From command line.
cp /tftpboot/cisco_util/* /tftpboot
Then reboot the phone. After the phone has upgraded the firmware. Type the following so the phone will
boot normally.
rm /tftpboot/xmlDefault.CNF.XML
rm /tftpboot/XMLDefault.cnf.xml
4.2.2
Polycom
http://www.voip-info.org/wiki-Polycom+Phones
5
Configuring and using Asterisk@Home features
5.1
Conferencing
Each extension you create will have its own conference. For example extension 200
has conference 8200. Just dial 8200 to get into your conference. If you dial
from 8200 you are the moderator.
You need to set a password for the meetme user. Type passwd-meetme from the
Linux command line.
Once you have started a conference you can manage it from the WebMeetme page.
Just enter the extension for the conference.
External access for conferences is disabled for security reasons. It is not
always desirable for people outside the system to have access to conferences
5.1.1
External access to conferences
If you want dial in access to conferences you need to be add an option on one
of the auto attendants for this.
First go into the Maintenance page and select Edit configs. The
file you want to edit is extensions_custom.conf add these lines to the
bottom of the file. Update the file and reload configs.
[custom-meetme]
include => ext-meetme
exten => s,1,BackGround(enter-conf-call-number)
exten => h,1,Hangup()
Next go into setup and Create a Digital receptionist if you
have not already done so. Record a main message for your receptionist. Something
like "press # for a company directory or press 1 to enter a conference" click
continue and Select 1 for number of menu options.
Next you will have to select an Action for this menu item. Click
Custom App and type in custom-meetme,s,1 then click continue.
That should be it when you dial in you select 1 from the main menu and you
will be prompted for your conference number. You can dial 7777 from and
extension to simulate an incoming call.
5.2
AMP (Asterisk Management Portal)
AMP is a web GUI that allows the configuration of Asterisk without the need
for editing config files. If you use AMP be careful not to make manual changes
to the config files that will affect AMPís operation. You can learn more
about AMP from their web site.
http://amp.coalescentsystems.ca/
5.3
DHCP server
Asterisk@Home has a built in DHCP server. This can be used to configure your IP phones.
The DHCP server is disabled by default. To make it active type
setup-dhcp
from the Linux command line. You must then
edit the
/etc/dhcp.conf
file and set it to match your network. On line 4 set up your network address and
netmask. On the next few lines enter the setting you want sent to your clients.
Edit line 15 and add a range of IP address to give out.
Remember to disable
any other DHCP servers you have on your network. These may include a Linksys
router or Windows internet sharing PC. Reboot your
Asterisk@Home system.
5.4
Flash Operator Panel
Flash Operator Panel is a real-time web interface for Asterisk. You can see
what all of your extensions, trunks, and conferences are doing. We have
extension 200 set up for testing. This is a live extension and will work
as soon as a phone is registered to ext 200. The rest of the buttons are
dummy objects for examples.
The op_buttons.conf file has all of the configs for each button in Flash
Operator Panel you can edit this using the Config Edit button on the maint
menu. You must reboot Asterisk or restart the panel service after you
make changes. The normal config files for Flash Operator Panel end in .cfg
we changed them to .conf so they would match the other files.
See the Flash Operator Panel we site for more info on Flash Operator
Panel. http://www.asternic.org/
5.5
FTP server (vsftpd)
Asterisk@Home has an FTP server that is used primarily for
configuring phones that use FTP such as Polycom. For security reasons
only one user is configured by default to user ftp. This user is ftpuser
(password: asteriskftp). It can access file in the /var/ftp directory. If
your would like other users to have ftp access add them to the /etc/vsftpd.user_list
file.
5.6
Cisco XML Services
Asterisk@Home has a Cisco XML Services that can be used to look up contacts
in a database. Click on CRM from the Asterisk@Home main menu.
(user: admin password: password) and enter all of your contacts and their
phone numbers.
Use the setup-cisco command to set up SIPDefault.cnf for your
Cisco phones. The setup-cisco script will set your
Services URL to http://ipaddressofyourasteriskbox/cisco/directory/services.php
you can then use the Services button of your Cisco phone to call your contacts.
5.7
Music On Hold (mpg123)
Asterisk@Home has now uses mpg123 for music on hold. Put a call on hold
and they hear music not dead air! See
voip-info.org for more info.
www.voip-info.org
music on hold info
5.8
Fax support (SpanDSP)
SpanDSP allows Asterisk to receive faxes. This service must be
installed. Type install-pdf from the command line. You can set this up in AMP.
xPL is a very simple and powerful home automation protocol. It can be used it
interface Asterisk into an existing home automation system. For example if you get
a call your
TiVo can display the caller ID info on your TV screen and turn down the stereo.
If you have a Microsoft based home automation system see the xPL project page (http://www.xplproject.org.uk/).
If you have a fully Linux based system MisterHouse (http://www.misterhouse.net)
has a good xPL interface.
One of the best features of xPL is the ability to mix and match applications. A
few Windows apps, MisterHouse on Linux, Asterisk@Home on CentOS, and a TiVo can
all be on the same network and share xPL information.xPL is not running be
default. To enable it type cd /usr/src/xplast then type ./install.sh
Once xPL is installed and running it will send out xPL heartbeat messages.
xPL will also send out notification of new voicemail messages. xPL can also send
out callerid info for any incoming calls. you must add a line to extensions.conf
to make it do this. Add this line to extension.conf at a location where you want
the callerid sent out.
exten => s,1,AGI,xplring.agi
For example a good place to add this line is to the [from-pstn-timecheck]
section. Be sure to renumber the following lines.
[from-pstn-timecheck]
exten => .,1,Goto(s,1)
exten => s,1,AGI,xplring.agi
exten => s,2,GotoIf($[${IN_OVERRIDE} = forcereghours]?from-pstn-reghours,s,1:)
exten => s,3,GotoIf($[${IN_OVERRIDE} = forceafthours]?from-pstn-afthours,s,1:)
exten => s,4,GotoIfTime(${REGTIME}|${REGDAYS}|*|*?from-pstn-reghours,s,1:)
exten => s,5,Goto(from-pstn-afthours,s,1)
5.10
Sugar CRM
SugarCRM is a complete CRM (Customer Relation Management) system. Although most of the feature of this software package are beyond the needs of home users the contact management module
in this package is the best we have ever seen in a web application. SugarCRM also has sophisticated user management.
Asterisk@Home uses SugarCRM mainly to manage contacts. SugarCRM is integrated into the Cisco XML phone directory making it possible to look up CRM contacts from a Cisco phone.
We have also added a click-to-dial function to CRM so that you can dial contacts directly from the web interface.
The default account for CRM is admin with a password of password. Once you have logged in you can create CRM users. You should make a CRM user for each extension. Enter the extension of a phone when you create a user so Asterisk will know where to send click-to-dial calls for that user.
Use standard Asterisk notation for extensions. For example for sip extension 200 enter
SIP/200 in the extension field.
6
Asterisk@Home add-ons
These add-on packages are not included with the Asterisk@Home iso. They can be
installed to add functionality to your Asterisk@Home system.
6.1
Click-to-Dial using Microsoft Outlook and AstTapi
AstTapi is a
Microsoft TAPI to Asterisk bridge that makes it possible to do
click-to-dial from Microsoft Outlook and other TAPI compliant
applications.
Download it from
http://sourceforge.net/projects/asttapi/
First make a login for AstTapi. Use the
config editor to edit
manager_custom.conf
There is a default AstTapi account you can use. Just remove the
#
from the
permit line and change the
192.168.1.0 to the
network address of your network. Then reload Asterisk.
Install AstTapi
In outlook click on a contact and click on the phone icon. Select a
phone number.
In the
"new call" dialog box select dialing options.
In the "
connect using line" box drop down and select Asterisk.
Click on line properties.
Host: <ip of Asterisk server>
Port: 5038
User: AstTapi
Password: AstTapi
User Channel: sip/200 (your extension)
Select
dial by context
Enter
outbound-allroutes in the context box
Click Apply
You can now make calls from Outlook!
6.2
H.323 add-on
This package adds H.323 support to Asterisk it also install the GnuGK
H.323 gatekeeper.
Installation
Copy the
asteriskathome-h323.zip file to you Asterisk@Home server using
WinSCP. Unzip the file by typing
unzip asteriskathome_h323.zip
from the command line. Next type
./install.sh
When the install is done reboot your Asterisk@Home system.
Testing
register a SIP phone with Asterisk@Home
open Microsoft Netmeeting click on tools -> options -> Advanced calling
Under Gateway Settings check off Use a gateway and enter the ipaddress
of your Asterisk@Home system.
Click OK
The calls from the gatekeeper will be put in the from-pstn
context. Make sure you have an incoming call route set up so the
calls have some place to go.
go back to the main NetMeeting screen and type in the extension of your
sip phone. You should be connect to your incoming call route.
For support try
The asterisk-oh323 project home page
http://www.inaccessnetworks.com/projects/asterisk-oh323
GnuGK home page
http://www.gnugk.org/
6.3
Webmin - web based Linux management
Webmin in a great package for managing a Linux box from the web. Webmin make it easy to configure application like SMTP mail. To install Webmin download the latest RPM from their web site and install it.
http://www.webmin.com/
Example
wget http://unc.dl.sourceforge.net/sourceforge/webadmin/webmin-1.220-1.noarch.rpm
rpm -Uvh webmin-1.220-1.noarch.rpm
7
Non-standard Hardware
Asterisk@Home is designed to work "out of the box" with standard PC hardware such as an Intel 1GIG PIII system.
Here is some info on how to get it to work on other hardware.
7.1
VIA EPIA 800 mhz board (586 board)
Asterisk@Home can run on 586 hardware. you must change the Asterisk Make file and recompile.
Load Asterisk@Home on your system. Asterisk@Home will not start.
CD to /usr/src/asterisk and edit the Makefile
Remove the # in front of the line "PROC=i586"
type
cd ..
then
./rebuildastsrc.sh
8
Useful Info for Asterisk@Home
8.1
Feature Codes - List
*411 Directory
*43 Echo Test
*60 Time
*61 Weather
*62 Schedule wakeup call
*65 festival test (your extension is XXX)
*70 Activate Call Waiting (deactivated by default)
*71 Deactivate Call Waiting
*72 Call Forwarding System
*73 Disable Call Forwarding
*77 IVR Recording
*78 Enable Do-Not-Disturb
*79 Disable Do-Not-Disturb
*90 Call Forward on Busy
*91 Disable Call Forward on Busy
*97 Message Center (does no ask for extension)
*98 Enter Message Center
*99 Playback IVR Recording
666 Test Fax
7777 Simulate incoming call
If you found this documentation helpful please consider making a donation to
the Asterisk@Home project:
http://sourceforge.net/donate/index.php?group_id=123387

![[Warning]](./stylesheet-images/warning.png)
![[Warning]](./stylesheet-images/caution.png)
